Atomic Structure Of Ceramic Materials

Copper has an atomic radius 0 128 nm a ccp crystal structure and an atomic weight of 63 5 g mol.
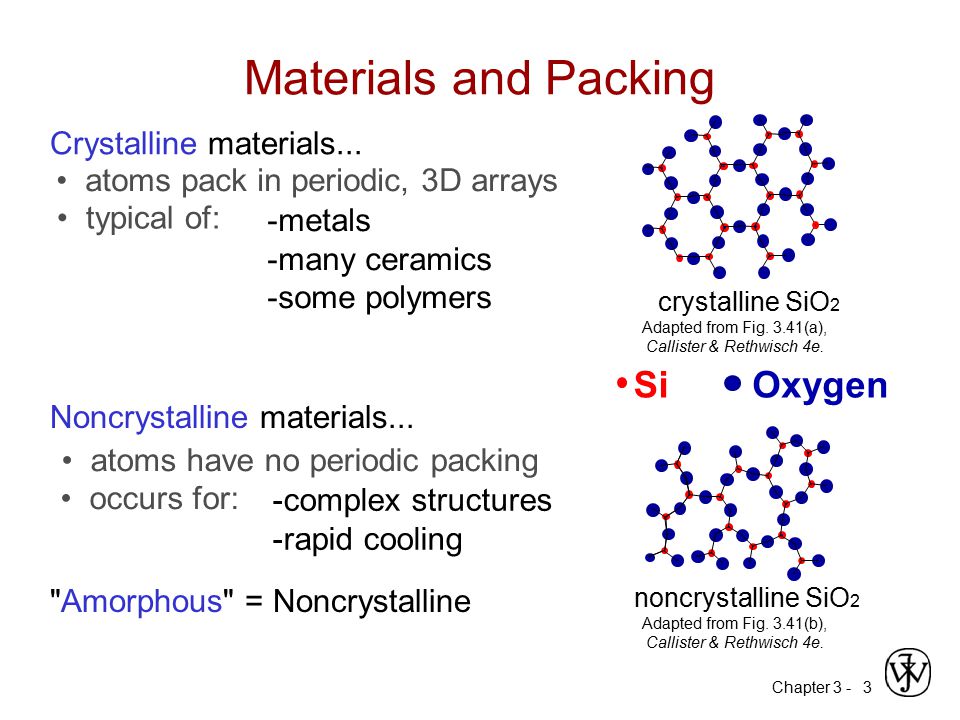
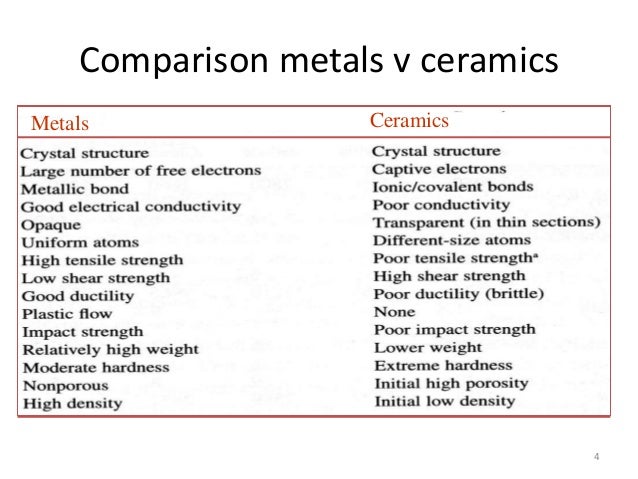
Atomic structure of ceramic materials. 1 structure john wiley and sons inc p. Types and applications of metal alloys. Structures properties of ceramics. In ionic bonding a metal atom donates electrons and a nonmetal atom accepts electrons.
Properties of materials vol. Structure and applications of metals. Electronic structure and atomic bonding determine microstructure and properties of ceramic and glass materials. Most ceramics are made up of two or more elements.
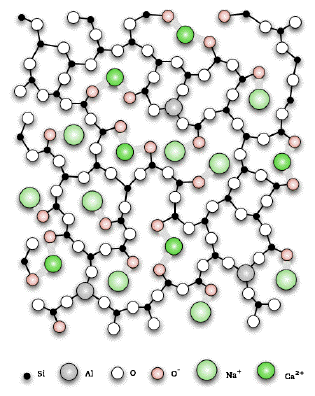
Atomic structure glasses are a unique range of ceramic materials defined principally by their atomic structure. Most ceramics usually contain both metallic and nonmetallic elements with ionic or covalent bonds. Industrial ceramics are commonly understood to be all industrially used materials that are inorganic nonmetallic solids. Glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous structure.
Atomic radius nm crystal structure metal example density of cu if you know the crystal structure the atomic radius and the atomic weight you can calculate the density of a particular metal. Atomic structure and bonding. Structure and applications of ceramics. As with metals the unit cell is used in describing the atomic structure of ceramics.
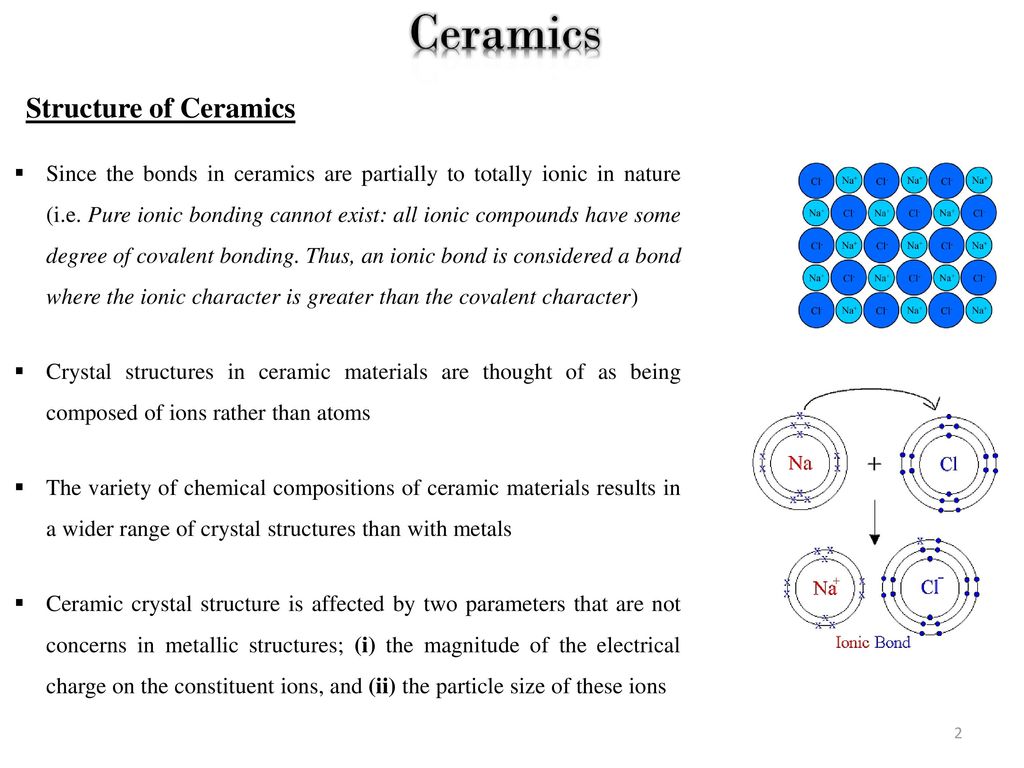
This electron transfer creates positive metal ions cations and negative nonmetal ions anions which are attracted to each other through coulombic attraction. Usually they are metal oxides that is compounds of metallic elements and oxygen but many ceramics. Ceramic composition and properties atomic and molecular nature of ceramic materials and their resulting characteristics and performance in industrial applications. For example alumina al 2 o 3 is a compound made up of aluminum atoms and oxygen atoms.
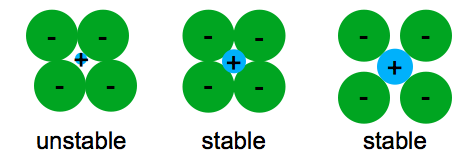
Recall that the predominant bonding for ceramic materials is ionic bonding. Just like in every material the properties of ceramics are determined by the types of atoms present the types of bonding between the atoms and the way the atoms are packed together. Therefore the structure the metallic atoms the structure of the nonmetallic atoms and the balance of charges produced by the valence electrons must be considered. What special provisions tests are made for ceramic materials.
Ac atomic weight of cation na number of anions in unit cell. 78 defects in ceramic structures. Economic environmental and societal issues in materials science. This is known as the atomic scale structure.
Ceramics are a little more complex than metallic structures which is why metals were covered first. A ceramic has traditionally been defined as an inorganic nonmetallic solid that is prepared from powdered materials and is fabricated into products through the application of heat.