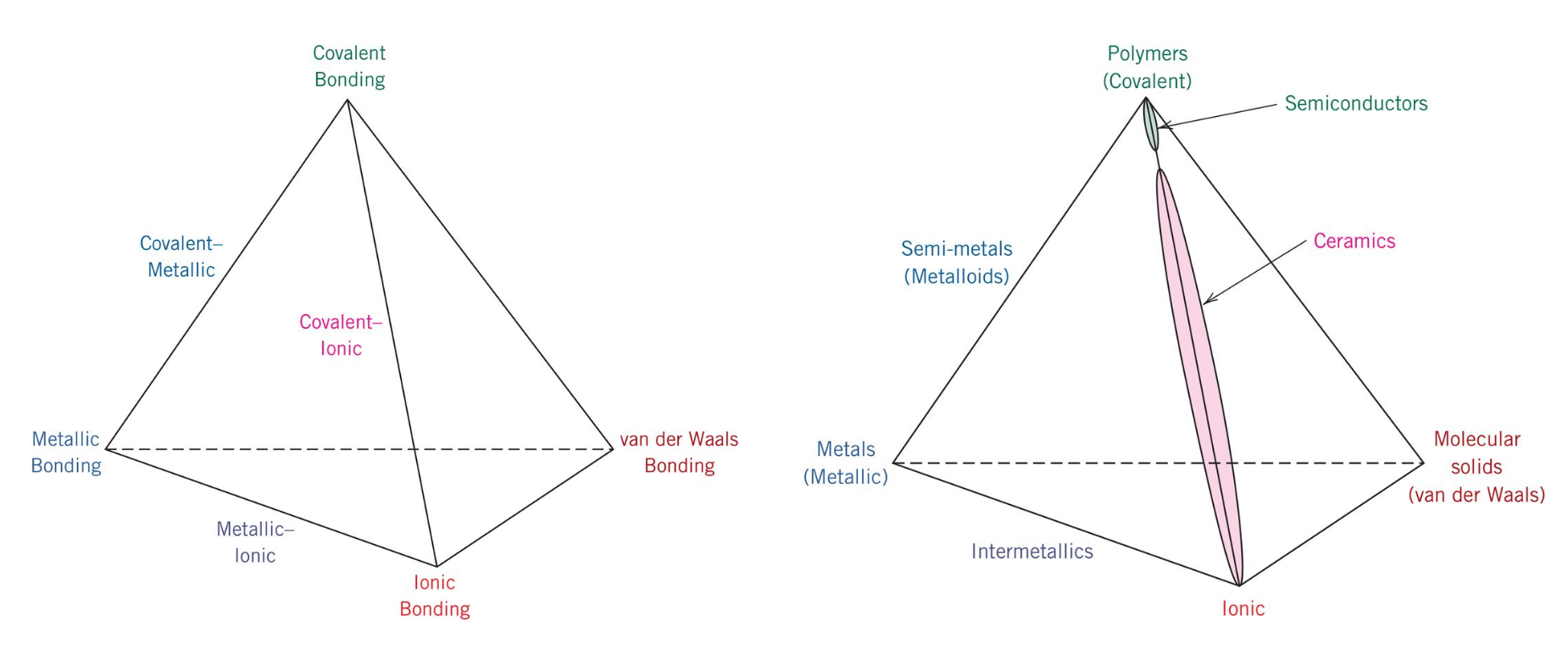
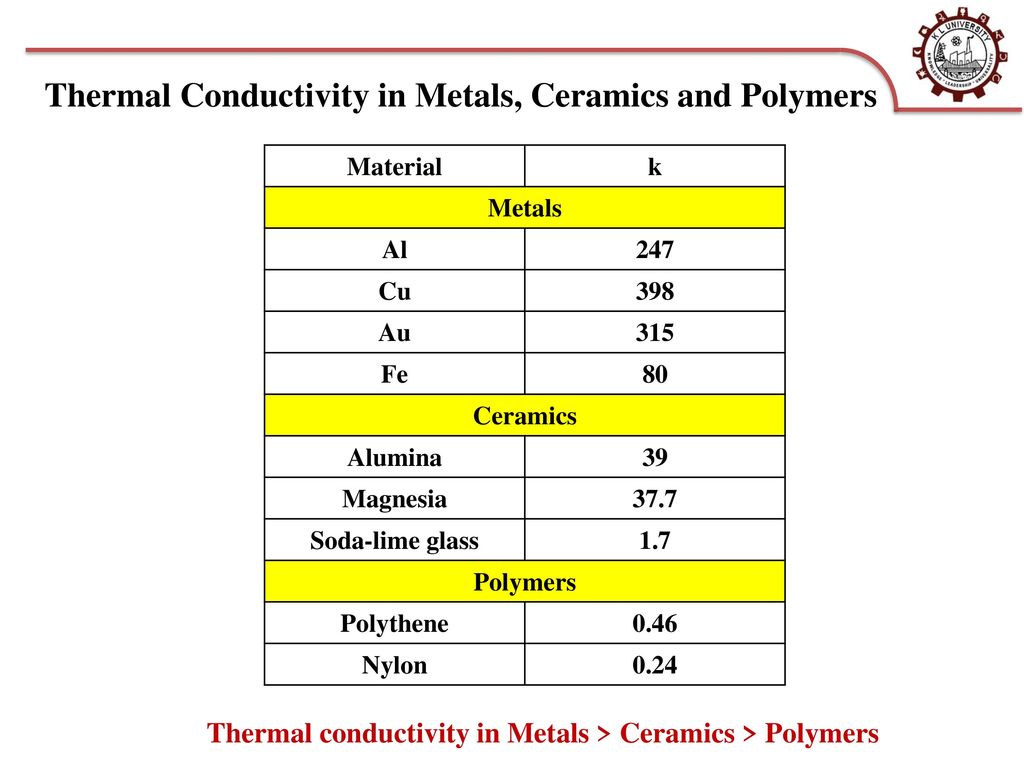
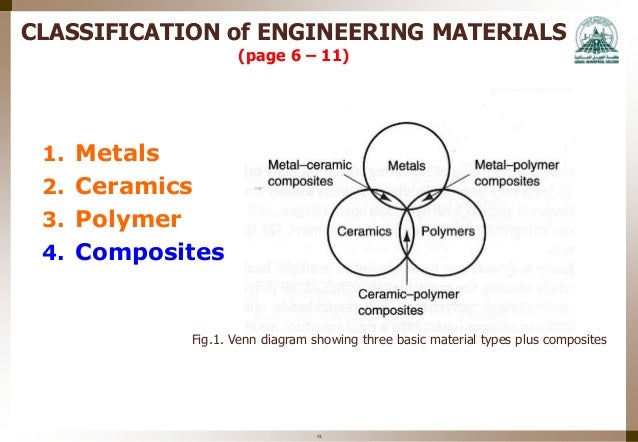
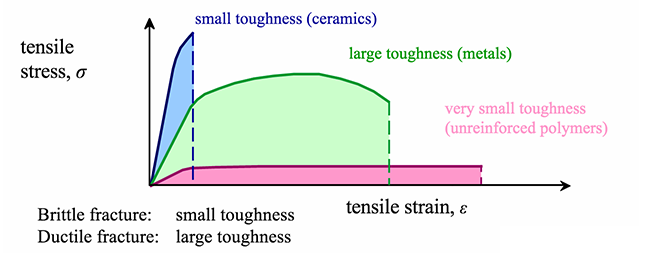
Atomic Structure Of Metals Ceramics And Polymers
Engineering polymers include natural materials such as rubber and synthetic materials such as plastics and elastomers.
Atomic structure of metals ceramics and polymers. In both ceramics and polymers creep depends on time and temperature. The key difference between polymers and metals is that the polymers are lightweight materials compared to metals. In fact properties of ceramics and glass can be tailored to specific applications by modifying composition including creating composite materials with metals and polymers and by changing processing parameters. If only one substance component is present the diagrams are simpler the axes are pressure and temperature areas represent single phases eg.
Solid liquid gas lines represent two phases in. Therefore the structure the metallic atoms the structure of the nonmetallic atoms and the balance of charges produced by the valence electrons must be considered. If we take a ball made of a polymer material such as plastic and a ball made of a metal with the same size we can observe that the metal ball is heavier than the plastic ball. Polymers are very useful materials because their structures can be altered and tailored to produce materials 1 with a range of mechanical properties 2 in a wide spectrum of colors and 3 with different transparent properties.
Creep is a time dependent factor due to deformation under stress or elevated temperature. As with metals the unit cell is used in describing the atomic structure of ceramics. The phase diagrams used to describe metals or ceramics or polymers are extensions of simple phase diagrams used for example for water figure 6a. Similar to metals and ceramics polymers can experience creep.
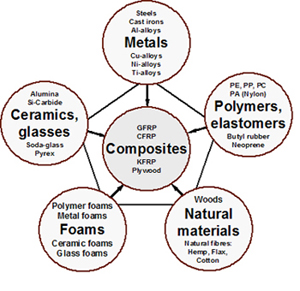
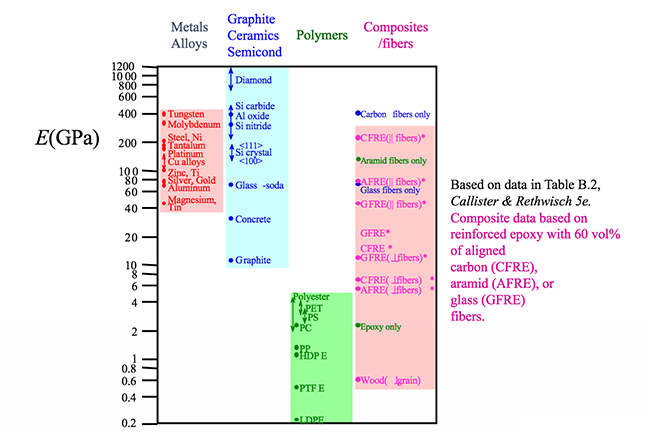
Composites properties very dependent on the particular reinforcement embedded in the matrix binder. The interdisciplinary field of materials science also commonly termed materials science and engineering is the design and discovery of new materials particularly solids the intellectual origins of materials science stem from the enlightenment when researchers began to use analytical thinking from chemistry physics and engineering to understand ancient phenomenological observations in. Polymers exhibit viscoelasticity at temperatures between where elastic and liquid like behaviors are prevalent. Atomic radius nm crystal structure metal example density of cu if you know the crystal structure the atomic radius and the atomic weight you can calculate the density of a particular metal.
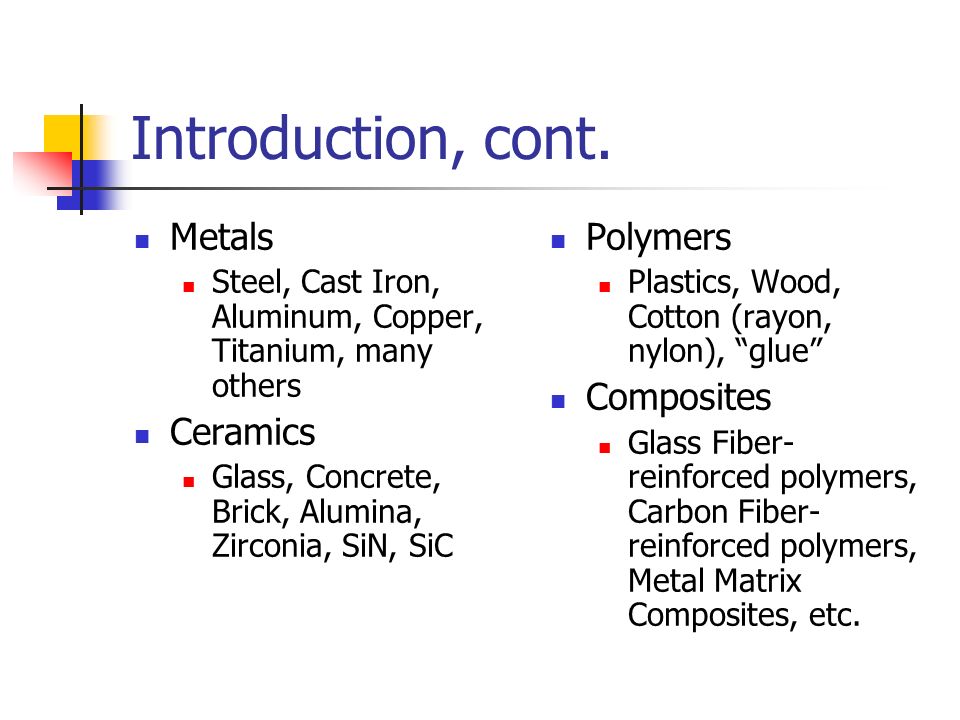
A comparison of four groups of materials. The table below provides a summary of the main properties of ceramics and glass. Therefore this property of the polymer is highly advantageous because we can replace metal with plastic. Copper has an atomic radius 0 128 nm a ccp crystal structure and an atomic weight of 63 5 g mol.
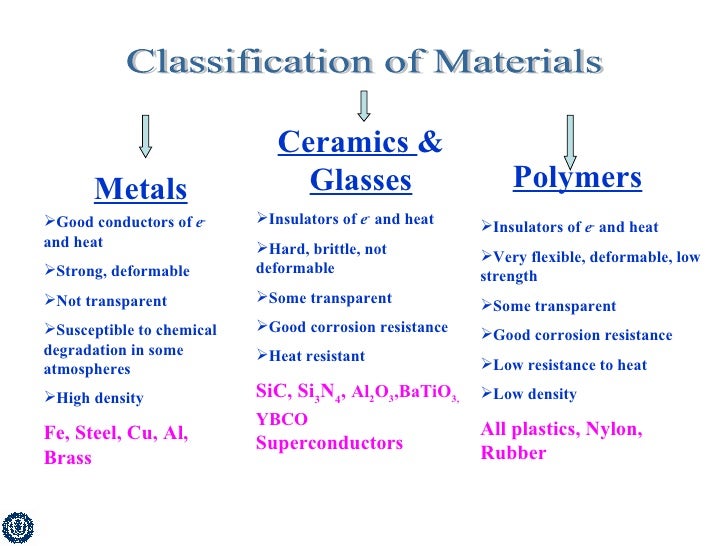
Metals many similar properties but alloys have very variable strength and melting point 2. These are typical properties.