Atomic Point Defects In Ceramics

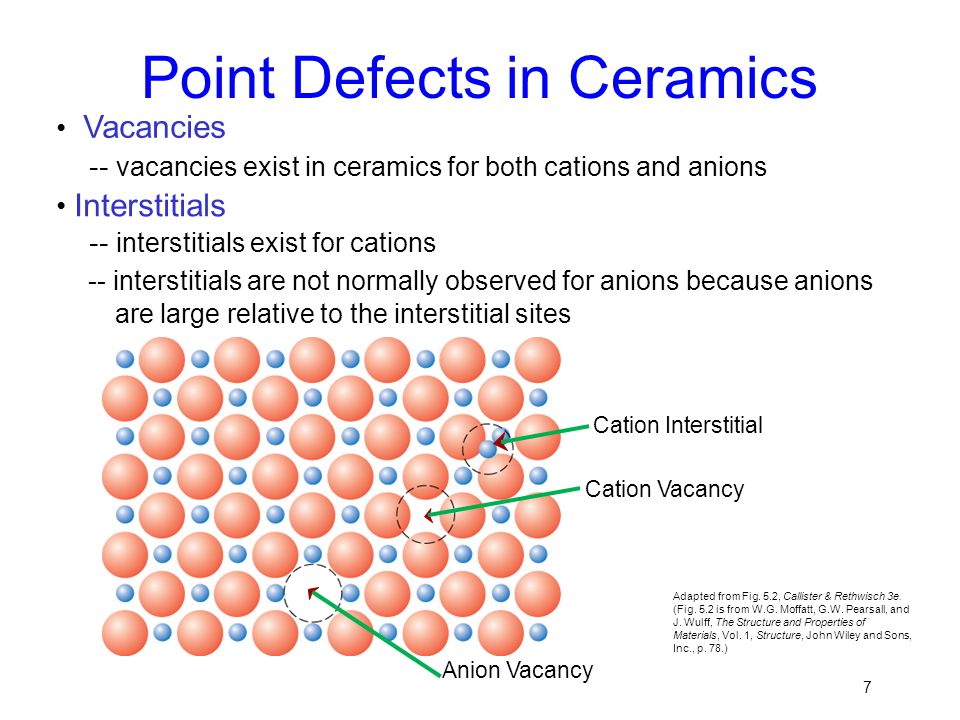
A principle difference between point defects in ionic solids and those in metals is that in the former all such defects can be electrically charged.
Atomic point defects in ceramics. The response was found to involve surface reconstruction and marked dimensional changes. Dimensional ranges of different classes of defects. Vacant atomic sites in a structure. So one schottky defect leads to the formation of two vacancies.
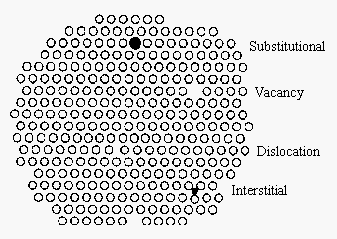
Schottky defect point defect in ionic crystal ceramic it is one type of point defect that occurs in ionic crystals ceramics. Defects and impurities in ceramics atomic point defects vacancies. Point defects i vacancies. Substitutional and interstitial atoms line defects dislocations area defects grain boundaries.
Point defects include self interstitial atoms interstitial impurity atoms substitutional atoms and vacancies. Point defects vacancy atoms self interstitial atoms impurities. The ionic and covalent bonds of ceramics are responsible for many unique properties of these materials such as high hardness high melting points low thermal expansion and good chemical resistance but also for some undesirable characteristics foremost being brittleness which leads to fractures unless the material is toughened by. Frenkel defects schottky defects.
A self interstitial atom is an extra atom that has crowded its way into an interstitial void in the crystal structure. Schottky defect occurs when oppositely charged atoms cation and anion leave their corresponding lattice sites and create a pair of vacancy defects. Point defects are where an atom is missing or is in an irregular place in the lattice structure. Ionic defects are point defects that occupy lattice atomic positions including vacancies interstitials and substitutional solutes.
Reviewed by faculty from. Vacancy distortion of planes self distortion. Describes vacancy and interstitial defects in a salt crystal. Imperfections in ceramics imperfections in ceramic crystals include point defects and impurities like in metals.
Electron irradiation point defects and surface reconstruction the response of nanotubes to uniform atom loss was observed. However in ceramics defect formation is strongly affected by the condition of charge neutrality because the creation of areas of unbalanced charges requires an expenditure of a large amount of energy.