Anatomy Of Floor Of Mouth Radiology

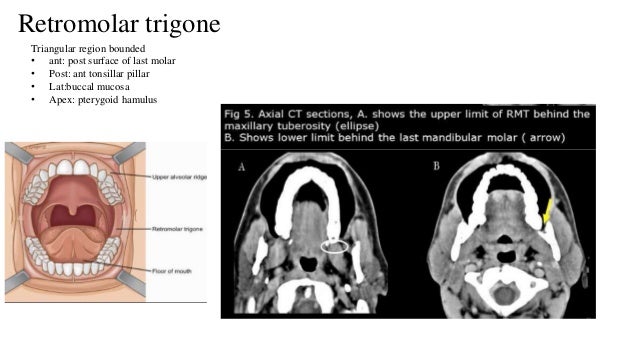
Its posterior border is the anterior tonsillar pillar.
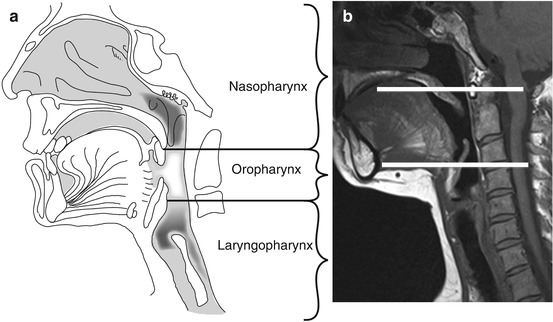
Anatomy of floor of mouth radiology. These include the hard palate floor of the mouth buccal mucosa including the upper and lower gingivobuccal sulci retromolar trigone and anterior two thirds or oral portion of the tongue and lips figs. The floor of the mouth fom is a u shaped area beneath the oral tongue. The floor of mouth is an oral cavity subsite and is a common location of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Thirty three first year medical students learned floor of mouth scan technique and ultrasound anatomy through a brief powerpoint module.
The mucosal surface of the floor of the mouth is easily examined clinically as superficial abnormalities can be assessed visually without the aid of imaging. Floor of the mouth. The oral cavity encompasses several relatively discrete regions. This study describes a self guided activity for learning floor of mouth ultrasound.
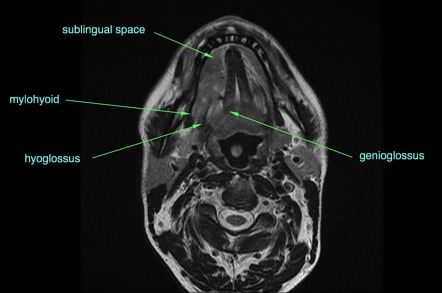
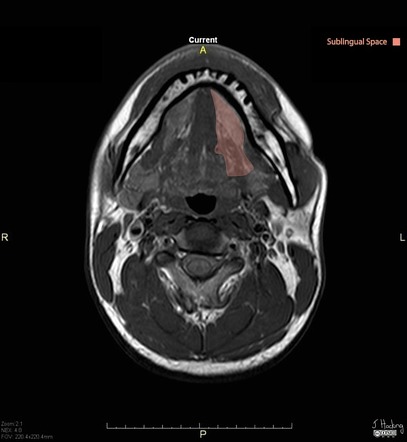
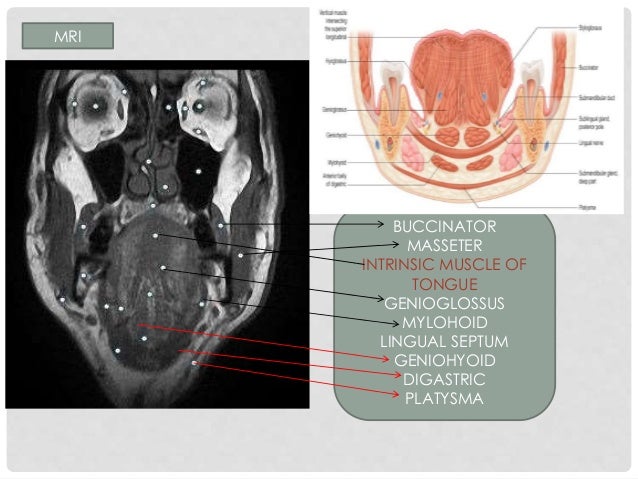
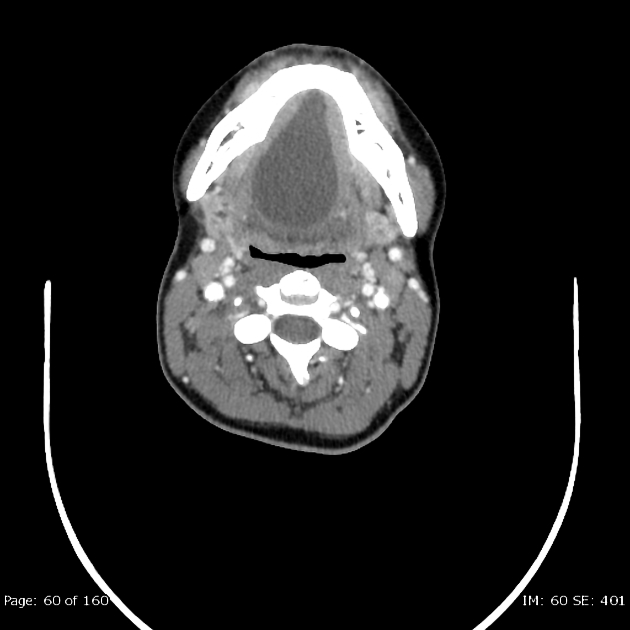
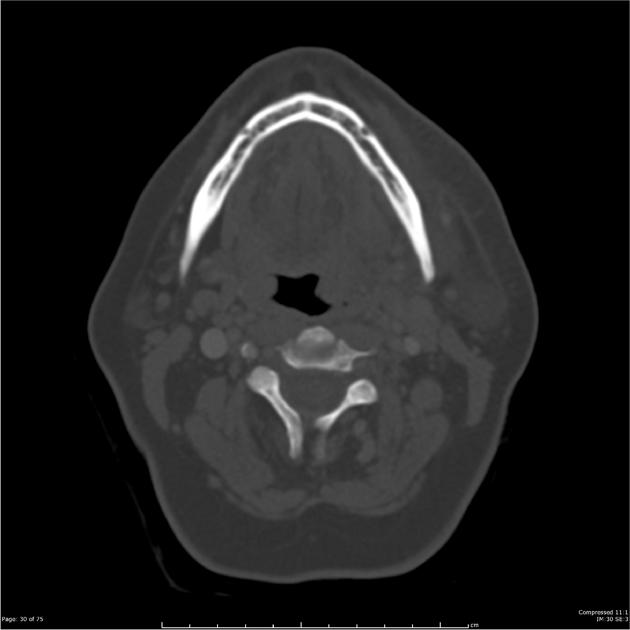
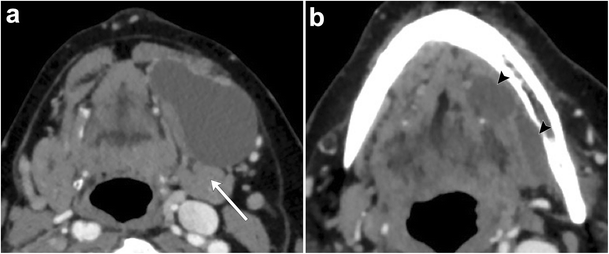
The floor of the mouth is the part of the oral cavity that is located under the tongue. The anatomy of the tongue and floor of the mouth is readily discernible by computed tomography ct because of low density fascial planes that outline the extrinsic musculature lingual arteries and hypoglossal nerves. Ultrasound is an active learning tool that can be used to supplement didactic instruction. Computed tomography ct and magnetic resonance mr images through the fom and oral tongue show the fom as a roughly symmetric region separated by a midline fatty lingual septum.