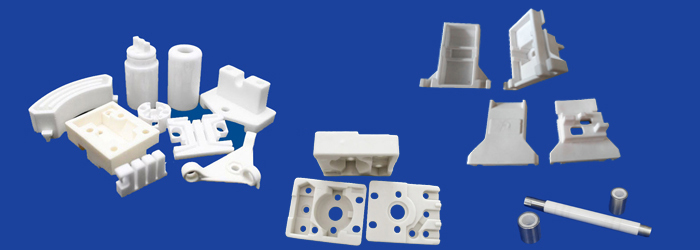
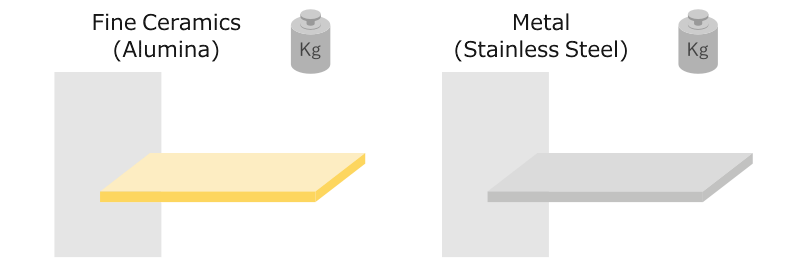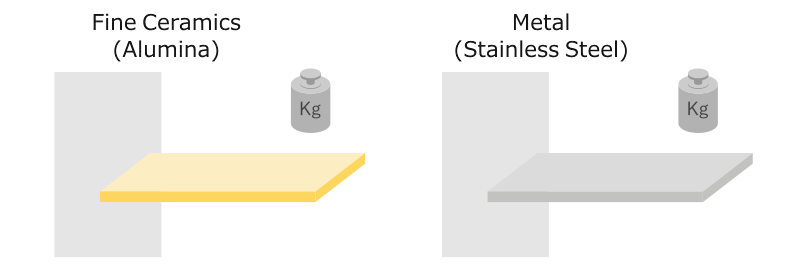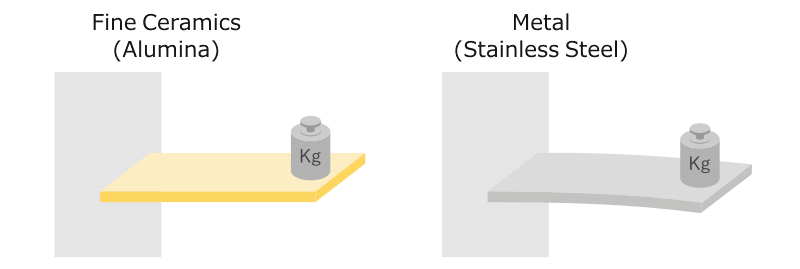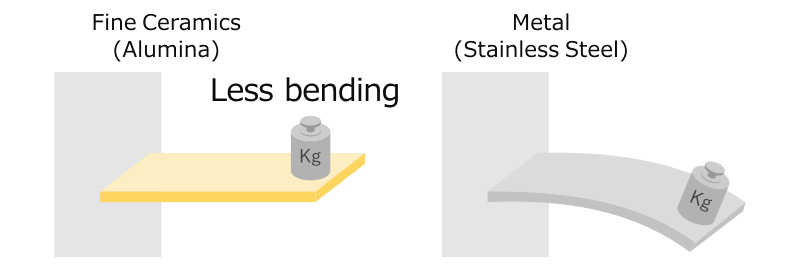
Alumina Ceramics Definition

Kinetics and thermodynamics studies of cobalt ii adsorption onto alumina.
Alumina ceramics definition. Alumina ceramic is relatively inexpensive readily obtained and has metallization schemes compatible with the user friendly 94 to 97 compositions that can be commercially obtained. The fledgling alumina ceramics industry began in the 1950s. Aluminum oxide ceramic or alumina is the preferred nonmetal choice for many structural ceramic components and high voltage insulators. They withstand chemical erosion that occurs in other materials subjected to acidic or caustic environments.
Alumina also known as aluminum oxide is a hard wearing advanced technical ceramic material frequently used in a wide variety of industrial applications. A ceramic material is an inorganic non metallic often crystalline oxide nitride or carbide material. Thus this book represents a major update on alumina ceramics. It has the same sintered crystal body as sapphire and ruby.
Some elements such as carbon or silicon may be considered ceramics ceramic materials are brittle hard strong in compression and weak in shearing and tension. Transparent alumina is currently one of the most mature transparent ceramics from a production and application perspective and is available from several manufacturers. It is 35 years since the last book dedicated to alumina ceramics was published at which time the alumina ceramics industry was still quite rudimentary with a primary focus on refractories and electrical insulators. Alumina synthetically produced aluminum oxide al2o3 a white or nearly colourless crystalline substance that is used as a starting material for the smelting of aluminum metal.
Aluminas are used in both general use and specialized applications. Higher purity alumina demonstrates enhanced wear and corrosion resistance creating a continuous scale of various alumina grades compositions and performance. Alumina definition the natural or synthetic oxide of aluminum al2o3 occurring in nature in a pure crystal form as corundum. Alumina is the most well known and most commonly used fine ceramic material.
Alumina al2o3 is extensively used as an adsorbent to remove metal ions dyes and organic solvents from solutions because of its higher porosity surface area and adsorption capacity 6. But the cost is high due to the processing temperature involved as well as machining costs to cut parts out of single crystal boules. It has been used for decades in electrical components for its high electrical insulation and is widely used in mechanical parts for its high strength and corrosion and wear resistance.